What is NPU
What is NPU
The embedded neural network processing unit (NPU) utilizes a "data-driven parallel computing" architecture and excels in processing extensive multimedia data, such as video and images.
Neural Processing Unit NPU, Artificial Intelligence AI and Machine Learning ML explained
Catalog
1. What is an NPU?
2. Processor modules of NPU
3. NPU: the core carrier of cell phone AI
4. NPU vs. GPU
5. The characteristics of different processing units
6. Practical applications of NPU
7. Explanation of each type of processing unit
1. What is an NPU?
The demand for neural networks and machine learning processing is just beginning to explode. While traditional CPUs/GPUs can perform similar tasks, NPUs, specifically optimized for neural networks, demonstrate much better performance than CPUs/GPUs. Over time, dedicated NPU units will gradually take over similar neural network tasks.
NPU (neural processing unit) is a specialized processor for network application packets that utilizes a "data-driven parallel computing" architecture, excelling at processing massive multimedia data such as video and images.
NPU is also an integrated circuit but differs from the single function of special-purpose integrated circuits (ASIC). Network processing is more complex and flexible. Generally, through special programming tailored to the characteristics of network computing, we can use software or hardware to achieve the specific purpose of networking.

NPU
The highlighted feature of the NPU lies in its ability to run multiple parallel threads--the NPU reaches another level with specific hardware-level optimizations that provide easily accessible caching systems for different processing cores. These high-capacity cores are simpler than typical "regular" processors because they do not need to perform multiple types of tasks. This set of "optimizations" makes NPUs more efficient, which explains why so much research and development focus on ASICs.
One advantage of NPUs is their emphasis on low-precision algorithms, new data flow architectures, or in-memory computing capabilities. Unlike GPUs, they prioritize throughput over latency.
2. Processor modules of NPU
The NPU is specifically designed for IoT AI to accelerate neural network operations and address the inefficiency of traditional chips in performing such operations. The NPU processor comprises modules for multiplication and addition, activation functions, 2D data operations, decompression, and more.
The multiplication and addition module is responsible for calculating matrix multiplication and addition, convolution, dot product, and other related functions. The NPU contains 64 MACs while the SNPU has 32.
The activation function module implements the activation function in the neural network using a highest 12th order parameter fitting. The NPU houses 6 MACs for this purpose while the SNPU has 3.
The 2D data operation module performs operations on a plane such as downsampling and plane data copying. Inside the NPU are 1 MAC and 1 SNUP for these tasks.
Lastly, the decompression module is utilized to decompress weighted data. To tackle the issue of limited memory bandwidth in IoT devices, weights in the neural network are compressed within the NPU compiler resulting in a compression effect of approximately 6-10 times with minimal impact on accuracy.
3. NPU: The Core Carrier of Cell Phone AI
As is well known, the normal operation of cell phones is inseparable from the SoC chip, which, despite being only the size of a fingernail cover, contains all the essential components. Its integrated modules work together to support the implementation of cell phone functions. The CPU is responsible for smooth switching of mobile applications, the GPU supports fast loading of game screens, and the NPU specifically handles AI computing and AI applications.
It is worth mentioning that Huawei was the first company to use NPU (neural-network processing units) on cell phones and integrate it into cell phone CPUs.
In 2017, Huawei introduced its own architecture NPU. In comparison with traditional scalar and vector computing modes, Huawei's self-developed architecture NPU utilizes 3D Cube for accelerated matrix computation. As a result, it can process a larger amount of data per unit time and possesses stronger AI arithmetic capabilities per unit power consumption, achieving an order of magnitude improvement compared to traditional CPUs and GPUs while also achieving better energy efficiency.
Huawei initially used Cambrian's NPU in Mate10 through an external approach. A year later, Huawei integrated Cambrian's NPU IP into 980. Subsequently, after another year passed by, Huawei shifted from using Cambrian to utilizing its own Da Vinci NPU in 990.
The Galaxy's NPU is built into their mobile processor to leverage advanced neural networks and provide a higher level of visual intelligence for models such as S20/S20+/S20 Ultra and Z Flip. The powering scene optimizer enhances content recognition in photos while prompting adjustments to ideal settings for subjects; this version boasts greater accuracy than previous Galaxy models did. Additionally enabling front-facing cameras to apply background blurring effects for selfies through bokeh effects- not only that but also integrates with Bixby Vision on-device .
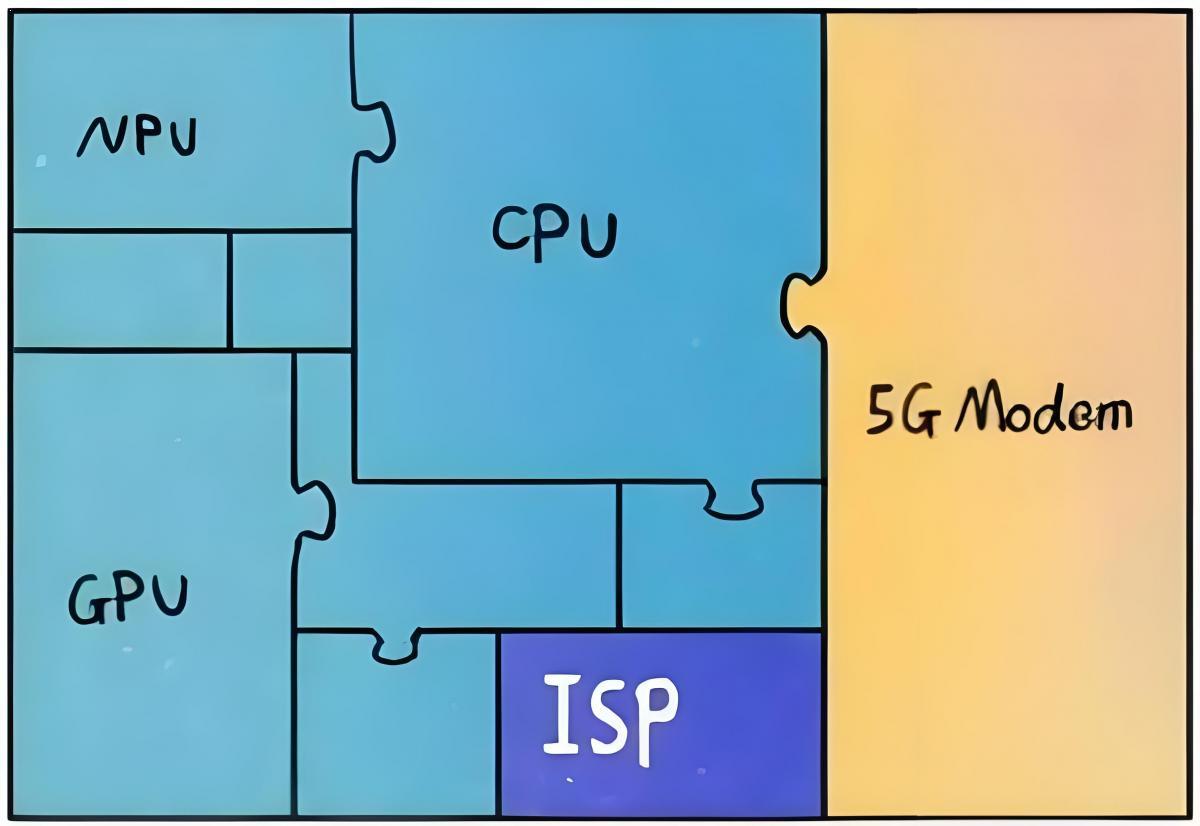
4. NPU vs. GPU
Although the GPU has an advantage in parallel computing capability, it does not operate independently and requires co-processing with the CPU. The construction of neural network models and data streams still occurs on the CPU. Additionally, there are issues related to high power consumption and large size. As performance increases, so does the size of the GPU, leading to higher power consumption and increased costs. This makes GPUs unsuitable for smaller devices and mobile devices.
Consequently, a dedicated chip called NPU was developed to address these challenges by offering small size, low power consumption, high computational performance, and high computational efficiency.