TDK Releases Pair of 6-Axis IMUs for Automotive Assistance and Safety
At this year's Electronica, TDK announced the addition of the IAM-20685HP and IAM-20689 six-axis MEMS inertial measurement units (IMUs) to its Invensense SmartAutomotive line of MEMS sensors. The two new MEMS devices provide more capable options over prior IMU offerings.

All About Circuits’ Jeff Child meets with the TDK team at Electronica 2024. Alberto Marinoni, quoted in this article, is to the right of Jeff.
TDK developed the IAM-20685HP specifically for ADAS applications, such as positioning and vision systems. It can achieve ASIL B on all technical safety requirements. The IAM-20689 adds more safety focus with additional embedded diagnostics to meet ASIL D requirements. It can be used in safety-critical applications like drive-by-wire or stability and roll control. Both parts are designed as Safety Element Out of Context (SEooC)
Key Features of the New MEMS IMUs
The IAM-20685HP and IAM-20689 both include 16-bit ADCs, programmable digital filters, and internal self-tests. They operate at 3.0 V to 5.5 V, with the same range for digital I/O. The current draw is less than 10 mA. They communicate via a 10-MHz SPI bus with CRC.
TDK designed the 20685HP for ADAS non-critical systems. It reaches ASIL B, which makes it a more economical component for vision stabilization, parking, navigation, and elements of autonomous driving that are not safety-critical. It includes lifetime fault detection with 20 internal safety mechanisms that can be accessed at startup or anytime during operation. They can also be set for continuous monitoring.
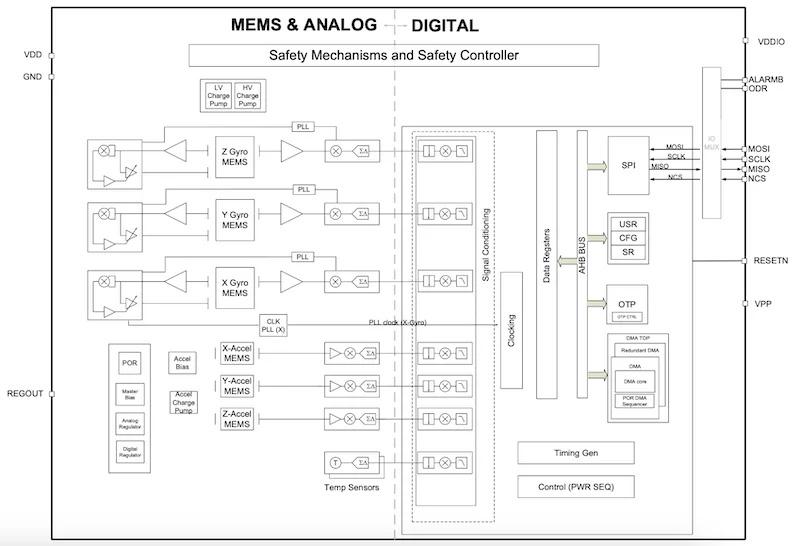
Block diagram of the IAM-20685HP. Image used courtesy of TDK
Because most applications today only require ASIL B, the extra cost of reaching ASIL D is not a common customer requirement. However, new designs are heading toward ASIL D. Developers can achieve the same functionality with higher safety ratings by taking the same die and adding additional safety features and ISO-required controls.
IAM-20689 is a safety-focused six-axis IMU featuring extended embedded diagnostics and greater design and manufacturing control to meet ASIL D. As an ASIL D component, the IAM-20689 can be used in any area of an ADAS system. It has the same size and functionality as the 20685HP but has 10 additional internal safety mechanisms.
The Significance of Six Axes
The two new TDK MEMS sensors combine a three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis gyro in the same package. This enhances safety, with each axis being a separate mechanical structure. A failure in one is unlikely to impact the other five.
Some applications require all six axes and, with most competitive solutions, will require a two-chip design. By putting all in one, the designer can reduce parts count and device size. Integrators have more flexibility in how and where to place the PCB in the car. The small 4.5 mm x 4.5 mm x 1.1 mm QFN package adds to that design flexibility.
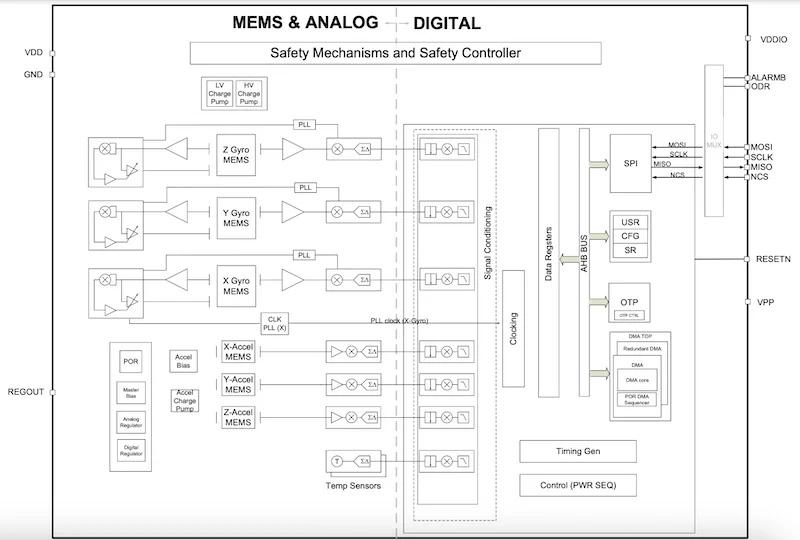
Block diagram of the IAM-20689. Image used courtesy of TDK
“As of yesterday, stability control and the rollover detection required two different components,” said Alberto Marinoni, TDK Invensense's senior director of automotive product marketing. “Having only three or five axes did not allow tier-one to measure all the dynamics of the vehicle in a single component. By having a single six axis in one central unit, you can combine stability control and rollover detection in the same central unit.”
Getting to the Bottom of Safety Classifications
ASIL is a risk classification scheme defined by ISO 26262 that identifies the amount of risk involved in the operation of an ADAS. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are ranked based on how much assistance the driver is given toward comfort and driving. ASIL ranks from A through D, with D being the greatest risk hazard rating. At ASIL D, as the IAM-20689 supports, a component malfunction has the “likely potential for severely life-threatening or fatal injury.” ASIL B, as the IAM-20685HP supports, indicates a lower risk level, such as losing a headlight or taillight.

TDK IAM-20685HP 6-axis IMU for automotive applications. Image used courtesy of TDK
For ADAS, the levels go from 0 to 5. ADAS 0 is a system that delivers information but no automation; the driver is 100% responsible for the vehicle's operation. ADAS 5 means full automation to the point that a steering wheel is optional.
SEooC refers to a component that is likely to be put into a safety-critical subsystem, but the component manufacturer doesn't know the specific subsystem for its end use. For example, TDK's two new parts may end up in a headlight aiming system, a parallel parking assist system, or a stability system. As long as the component meets the ASIL level of the end system, it can be used in a variety of non-specified applications.
ADAS With Options
TDK's two new MEMS IMUs give greater functionality than prior versions and competitive offerings. The two are similar, providing cross-familiarity for designers. With two ASIL-level options, designers have options for cost and maximum safety.



