TI Integrates Edge AI and Real-Time Control in New Mission-Critical MCUs
Today at Electronica 2024, Texas Instruments (TI) announced its new TMS320F28P55x series of C2000 MCUs. TI calls the series the industry’s first real-time microcontrollers with an integrated neural processing unit (NPU). Along with that announcement, TI also revealed the new 64-bit F29H85x series of MCUs built around its C29 digital signal processing (DSP) core. The C29 MCUs target automotive applications that require fault-tolerant, low-latency operations and predictive decision-making. Both sets of new MCUs can serve mission-critical applications that require low-latency, real-time detection, calculation, and response.
A Brief Introduction to the Two New MCU Series
The 40+ variants of the TMS320F28P55x series (datasheet linked) come with an integrated hardware NPU and on-chip Flash memory of up to 1.1 MB. This series also features 24 pulse width modulation (PWM) channels and 39 analog-to-digital (ADC) channels.

TMS320F28P55x and F29H85x MCUs. Image (modified) used courtesy of Texas Instruments
The second series of MCUs in this announcement, the F29H85x, provides motor and power control with two to three times the signal chain performance of its predecessors. TI also claims these devices have a five times faster fast Fourier transform (FFT) performance in diagnostics, tuning, and arc detection. Real-time interrupts run four times faster, and the MCUs are reportedly two to three times higher performing for general-purpose code execution. It includes an isolated hardware security module as well.
The TMS320F28P55x Series: Aided by a Powerful NPU
For over 25 years, TI's C2000 family has provided real-time control in industrial and automotive applications. The newest additions to the family, the TMS320F28P55x series, integrate an NPU as an edge AI hardware accelerator. The NPU enables the MCU to offload AI processing from the primary core to dramatically increase real-time performance. The NPU offers advanced AI-based decision-making without loading down the primary processing core.
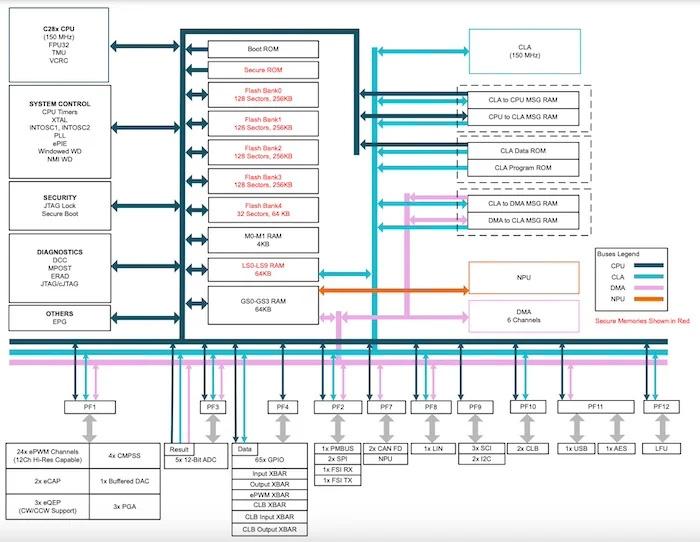
Functional block diagram of the TMS320F28P55x. Image used courtesy of Texas Instruments
Conventional microcontrollers use simple logic to make real-time decisions. They use combinations of “if-then” or state machines to evaluate conditions and essentially make Boolean logic decisions based on given sets of input conditions. When sensor input is obvious and accurate, this type of system can work quite well. However, with more sensors providing input and with fast-changing conditions, ambiguity or sensor lag can lead to invalid input conditions or improper results. With today’s stringent safety and efficiency requirements, Boolean logic is insufficient for many requirements. That’s where edge AI can deliver significant improvements.
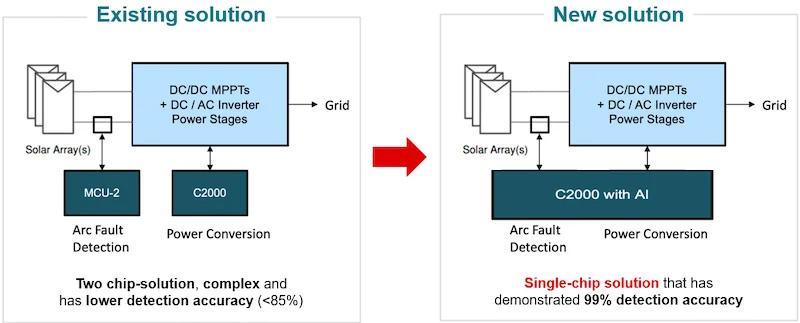
Adding NPU-based AI enables greater one-chip functionality with improved accuracy. Image used courtesy of Texas Instruments
TI notes that NPU capabilities will benefit applications like arc fault detection in solar and energy storage systems and motor-bearing fault detection for predictive maintenance. In both cases, conventional MCU code can misconstrue such faults, misidentifying them or not identifying them soon enough. The NPU allows the MCU to perform more advanced AI-style interpretation of sensor inputs in real time.
The TMS320F28P55x's NPU can also be trained to adapt to different environments with different sensor inputs, greatly increasing detection accuracy. It can run convolution neural network models to learn complex patterns from sensor data. The NPU will offload these calculations from the main CPU core and use AI to detect complex fault conditions, which can result in a five to 10x decrease in latency for detection operations.
The F29H85x Series: Leveraging 64-bit DSP and Real-Time Control
The F29H85x MCU uses TI’s new C29 DSP core to deliver more than double the real-time performance of its predecessor, the C28. The new F29H85x processor series with the C29 DSP core boasts TI’s very long instruction word (VLIW) architecture, which supports the execution of up to eight instructions per cycle. The MCUs offer cyber security features as well, including a fully isolated hardware security module to protect the system. Further, the hardware safety and security unit uses context-aware memory protection to extend hardware isolation to CPU tasks without interference. The architecture provides security without a performance penalty added to the rest of the MCU.
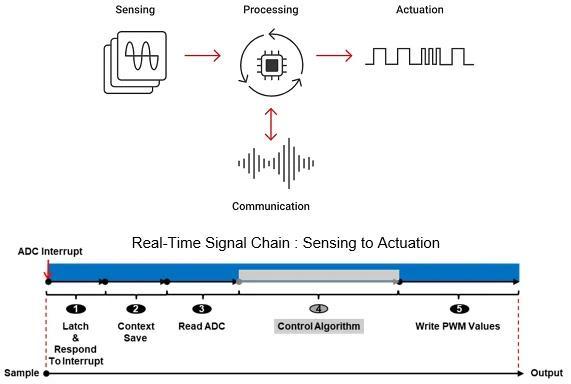
Improved C29 DSP core response receives, processes, and responds more than twice as fast. Image used courtesy of Texas Instruments
The 64-bit DSP with complex math ability can speed the signal chain performance for motor and power control by two to three times over the C28. It has five times the fast Fourier transform (FFT) performance. (FFT is used for systems diagnostics, tuning, and arc detection.) Interrupt response is four times faster than the C28 and general-purpose processing code can be executed two to three times faster.
TI engineered the chips to comply with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 26262 and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61508 automotive and industrial safety standards.

C2000 real-time MCU F28P55x development kit in TI LaunchPad form factor. Image used courtesy of Texas Instruments
The F29 processors are automotive safety integrity level (ASIL) D and safety integrity level (SIL) 3 certified. ASIL D is the highest of four automotive safety risk management levels. SIL 3 is an industrial standard for risk mitigation used in a number of industry standards. SIL has three levels, with three being the highest. Visit TI at its Electronica booth C4-158.