Three New Passives Flex High Performance in Ever Smaller Packages
Big silicon may get the glory in the technology world, but none of it would matter without passive components. In this roundup, we look at three passive components from TDK, Kyocera, and Littelfuse that push the limits in their respective categories. Each of these new parts is designed to extend innovation in size and capability.
TDK Introduces the 'Smallest Thin-Film Power Inductor'
TDK claims it has developed the smallest inductor for power circuits, measuring 0.80 x 0.45 x 0.65 mm. The new thin-film PLE856C Series inductor uses low-loss magnetic material and high-precision internal electrode formation to deliver high performance in the so-called industry’s smallest physical form factor.

TDK film PLE856C series inductor at 0.80 mm x 0.45 mm x 0.65 mm. Image used courtesy of TDK
With feature values from 470 nH to 1.5 µH, the new inductors target designs where size is constrained but performance can’t suffer. Examples of applications include wireless stereo earbuds, smartwatches, AR/VR devices, small power supply modules, and small communication modules.
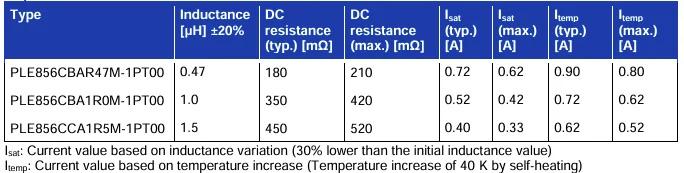
Key specifications for PLE856C Series inductors. Image used courtesy of TDK
While inductors often face obstacles to miniaturization, these inductors feature a 40% smaller mounted area and a 50% lower volume over TDK's prior small inductor series.
Kyocera Resistors Bring Higher Power to Small Packages
Kyocera recently introduced the "industry’s highest power-rated 0603 resistor." The new part is a member of the Kyocera CR series of resistors.

Kyocera's 2.6-W, high-frequency resistor in a 0603-package. Image used courtesy of Kyocera
The CR series parts are RoHS compliant, qualified for MIL-PRF-55342, and manufactured with ISO-9001 compliance. The CR series resistors target specialized high-frequency RF applications.
The 0603 parts come rated at up to 2.6 W, the highest power rating available in that package size. Kyocera increased the power rating by utilizing a high-thermally conductive substrate and increasing the heat sink grounding area. The new resistors come in standard values of 50 Ω and 100 Ω and 5% or 2% precision. The resistors are non-magnetic and constructed with thin-film aluminum nitride substrates and silver terminals.
The resistors are slated for applications such as high-power RF amplifiers and instrumentation, test and measurement, communications, and defense industries. In addition to RF amplifier applications, the parts are suitable for use as dummy loads, power measurement shunts, and resistive baluns for impedance matching.
The 0603-sized CR10603TxxxxJ resistors are part of a high-power surface mount product line that ranges from the new 2.6-W, 0603-size package to a 250-W, 3737-size package. The new 0603 addition enables greater miniaturization of RF and power devices than was previously possible.
Littelfuse's Diodes Protect SiC MOSFET Gate Drivers
Littelfuse has announced a new series of TVS diodes designed for protection circuits surrounding silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET gate drivers.

Littelfuse's TPSMB Asymmetrical TVS Diode Series. Image used courtesy of Littelfuse
As requirements for charging circuits, inverters, and other power systems increase, the supporting and primary active components must also improve. Littelfuse designed its new TPSMB Asymmetrical TVS Diode Series for just that purpose. SiC MOSFETs require clamping circuits between the gate and source for overvoltage and reverse surge protection. In high-power designs (including most SiC circuits), a combination of Zener diodes and TVS diodes protect the MOSFET from both negative and positive surge currents.
An asymmetrical TVS diode combines the functionality of both a Zener diode and a TVS diode in one package. SiC MOSFETs have specific negative and positive gate voltage ratings and requirements. Without an asymmetric part, the gates are protected with a Zener and TVS in series. Combining both into one package reduces parts count and increases the reliability of the circuit design. The asymmetry enables different positive and negative voltage clamping values. The new TVS diodes will be designed into circuits for onboard chargers (OBCs), EV traction inverters, I/O interfaces, and Vcc buses.
Continuing Innovations with Discrete Componentry
By bringing greater capability into smaller packages—like the TDK inductor and Kyocera resistor—or combining multiple duties into a single package, like the Littelfuse asymmetric TVS, passives companies are promoting continued progress in various electronic devices.




