The Evolution of Storage Devices: From Punched Cards to USB Mass Storage Devices and Beyond
Some people believe that "most technology products are destined to be open for only a short period of time." In this post, I will discuss the evolutionary history of storage devices in the age of technology.
Storage Devices
A Brief History of Storage Devices
The evolution of storage devices has been a continuous process since the earliest forms of media were used. The advent of the Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in the way data was stored with the development of mechanical devices. This article will examine the evolution of mechanical storage devices from the Industrial Age.
Punched cards and punched paper tapes represent the original mechanized storage form of information. In 1890, Herman Hollerith, an American statistician, invented the punch-card tabulating machine which could record up to 960 bits for collecting and counting census data. This marked the beginning of the era of semi-automatic data processing systems. These systems have gradually become widely used in industrial retrieval and data statistics.
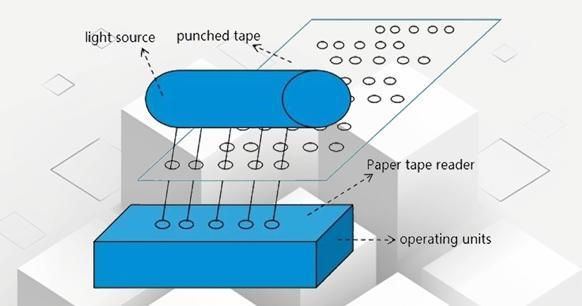
Punched Paper Tape Sequence Control Principle
Punched cards and punched paper tapes are used in punch card tabulation machines as input and output devices of early computers. They convert programs and data into binary codes where holes are 1 and non-holes are 0 and then input into the computer through photoelectric scanning.
The magnetic tape marked the beginning of the era of magnetic storage.
In 1928, Fritz Pfleumer, an engineer from Dresden, Germany, invented the audiotape which can store analog signals. The working principle of the magnetic tape is as follows: the crushed magnetic particles are glued to the paper strip to prepare the magnetic tape. However, due to the fragile paper strips, audiotapes were not practical at that time. In 1951, magnetic tapes were introduced for computer data storage. One magnetic tape could replace 10,000 punched paper cards. In 1980, a small cassette tape was developed. A 90-minute tape can record approximately 660KB of data on each side.

Magnetic Tape
Drum Memory:
The Predecessor of Hard Drives Prior to the advent of magnetic core memory, the magnetic drum was widely used in computer memory and was considered the predecessor of hard disk drives. The magnetic drum offers several advantages including practicality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. However, its storage capacity is limited and its utilization rate is relatively low.

Drum memory
Magnetic core memory is an early version of random access memory (RAM). In 1949, Dr. An Wang from the Harvard University Laboratory in the United States developed the "read and write" technology for magnetic core memory. The principle of magnetic core memory is that the magnetic core can produce two opposite directions of magnetization according to the direction of current during magnetization and use this as a state of 0 and 1 to record data. The original magnetic core memory had a capacity of a few hundred bytes. Magnetic core memory was widely used as the main memory of computers in the 1970s until Intel’s semiconductor DRAM memory was mass-produced.
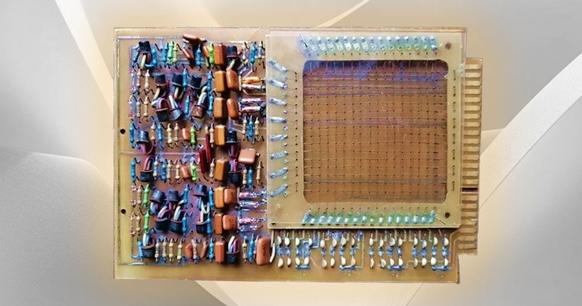
Magnetic Core Memory
Hard Disk Drive-Disk Storage Era
In 1956, IBM's Reynold B. Johnson led the R&D team to invent the world's first hard drive, the IBM 305 RAMAC. The drive is approximately the size of two refrigerators and weighs one ton. It contains 50 24-inch platters, has a capacity of only 5MB, and has a data transfer speed of 10K/S. Currently, desktop hard drives are typically 3.5 inches in size and products with a capacity of 18TB have also been developed. The hard disk drive marked a significant leap in storage technology, offering a practical solution to clearing as device storage for large-scale data.

Hard Disk Drive
Floppy Disk—The earliest removable medium used in personal computers
In 1971, floppy disks were introduced by IBM and were widely used from the mid-1970s to the late 1990s. Initially, they were 8-inch disks followed by 5.25-inch and 3.5-inch disks. The earliest read-only floppy disk had a capacity of 79.9 KB in 1971 and a readable and writable version appeared one year later. Floppy disks have a slow access speed and a limited capacity but they are detachable and easy to carry, fitting well into the concept of removable storage devices folder for data transfer.
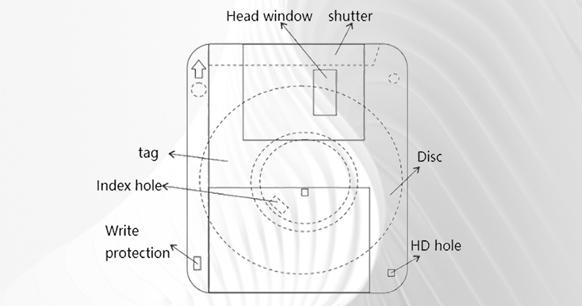
The 3.5-inch floppy disk structure
CD-ROM – the storage carrier of optical information
In 1982, Sony and Philips released the CDP-101, the world's first commercial CD audio player, and CD became popular. Early CDs were only used in the film industry with a diameter of 30 cm. Each side could record 60 minutes of video or audio. The storage density of CD technology has been continuously improved and CD-ROM, DVD, D9, D18, and Blu-ray technology have emerged. Game discs for game consoles, retail movies, and materials requiring long-term storage can still be found on the CD.

CD
Common storage devices in use today
With the advancement of computers and the Internet, the CD is becoming less relevant. The demand for information storage continues to increase, driving the accelerated evolution of storage devices. Let's now examine the storage devices currently in use.
Solid State Drive – Simplified Computer System
In 1989, the first solid-state hard drive appeared, also known as a solid-state drive. This was a hard drive made of an array of solid-state electronic memory chips. Since then, solid-state drives have gradually gained market traction and are now used in professional fields such as medical, aviation, and military applications. Compared with traditional hard disks, they offer several advantages including fast read and write speeds, shock and drop resistance, low power consumption, no noise, and light weight. However, they do have a limited lifespan due to the number of erasing and writing cycles they can withstand. Computer data storage devices abbr SSDs have become a standard in modern computing.

Solid State Drive (SSD)
SD card – a memory card based on semiconductor flash technology
In 1999, Japan's Panasonic, Toshiba, and SanDisk Corporation jointly developed an SD card. Initially, the capacity was only 2/4/8 MB and it has now reached 128/512 GB or even 1T in the continuous update of the standard. In the early days of mobile phones, when MP4 was a popular format for music and video, SD cards were the go-to solution for mobile data loading. Mobile phones were packed with more songs to act as a music player and MP4 could download more movies to act as a small TV.

SD Card
USB Flash Drive – a storage device using flash memory chips as storage media
In 1998, the USB flash drive was launched for the first time. In 2004, China Netac Technology Co., Ltd. obtained a basic invention patent for flash drives officially authorized by the US National Patent Office. The device is characterized by "small size, large capacity." It can be used to transfer files from a computer to a flash drive at any time simply by plugging and unplugging the device. Additionally, USB flash drives, bootable USB flash drives, anti-virus USB flash drives, temperature measurement USB flash drives, and music USB flash drives are also constantly being developed. However, users often encounter a problem ejecting usb mass storage device, a common issue during everyday use.

USB flash drive
New storage technologies looking to the future
The rapid development of cloud computing, big data, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence has ushered in the era of "information explosion." Information has exploded and storage is accelerating. It is believed that with the continuous advancement of technology, storage devices as carriers of information will also develop faster. Let's discuss the storage technology of the future.
Nano storage represents a significant potential area for future development.
In 1998, the University of Minnesota and Princeton University in the United States successfully developed a quantum disk, a nanoarray system composed of magnetic nanorods. A quantum disk is equivalent to our current 100,000 to 1 million disks while energy consumption has been reduced by 10,000 times.
In 2002, a research team from the University of Wisconsin in the United States developed an atomic-level silicon memory material with a density of information stored that was 1 million times that of the current optical disk.
In 2014, Professor Sharon Grotz of the University of Michigan discovered in a study that the combination of nanoparticles is like a Rubik's Cube twisting around a central point. This state change can be used to encode information like a string of 0 and 1.
Nano storage uses various methods to fundamentally improve storage capacity and replace existing storage media with ultra-high-density media and devices. This is a major development direction for future storage devices.
Cloud Storage: A Technology in Evolution
Finally, I will discuss cloud storage, which is a technology that is still evolving. In general, cloud storage is a system that allows users to store data on a collection of many storage devices and servers. Users can access this data from any networked device, making it convenient to access data from anywhere and at any time.

There are two main ways that cloud storage is implemented:
Public Cloud: In this implementation, a third party provides the storage as a service and the data is stored in a remote location. Users have no control over or understanding of the technology used in the cloud. Cloud storage is a common feature of modern life.
Private cloud: The data center is developed internally for enterprises and provides cloud services such as storage space applications and rapid deployment of enterprise application systems. At the same time, there are potential risks associated with cloud storage, including data infringement, the disclosure of personal and commercial data, data persistence, and continuous charging. As the Internet of Everything and the big data revolution continue to evolve, cloud storage technology will likely see further advancements.