Intel Rounds Out Xeon 6 Portfolio With New CPUs for AI and Networking
This week, Intel announced new Xeon 6 processors targeting a variety of HPC and AI applications. The steep demand for AI alongside 5G deployments has also increased the need for high-performance processors—something that Intel hopes to address with its newest offerings.

Intel designed its Xeon 6700 and 6500 processors to optimize power efficiency and performance.
We spoke with Intel representatives Ronak Singhal and Cristina Rodriguez to learn more about the new processors, their applications, and how they stack up against previous generations.
Generational Advancements
Intel has unveiled two new processor families: the Xeon 6700 and Xeon 6500, both of which join the Xeon 6900 as part of the broader Xeon 6 lineup. Compared to the flagship Xeon 6900, the Xeon 6700/6500 offers designers new levels of performance to optimize power, performance, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
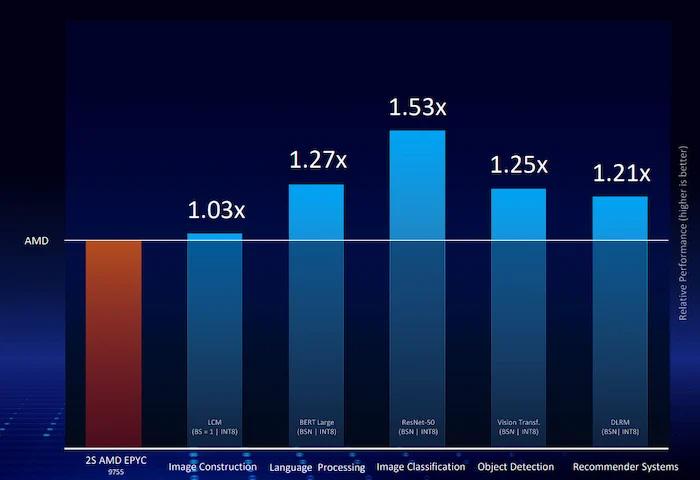
When stacked up against comparable processors, the Intel 6787P reports improved performance in AI-focused applications.
The Xeon 6700/6500 is available with core counts up to 86, supporting multi-socket architectures of up to eight sockets. The new Xeon 6 processors are also available in lower core counts for operators who do not need maximum core density.
“Intel has a significant volume in that 24 to 48 core range,” Singhal said.
Intel reports that the max TDP is 350 W for both processors, with eight channels of DDR5 and MRDIMM memory available. Finally, the processors support up to 136 PCIe 5.0 lanes with a single socket, providing architects with much more connectivity for future applications.
“A common question I get these days is, Why? Why are we still investing in systems that look like this with this degree of socket connectivity in the coherent space? As we grow the core counts, do people really need to have a four-socket system or an eight-socket system?” Singhal said. “I think the answer very simply is yes. We continue to see people who want to scale out their memory capacity. As you scale out that memory capacity, you can marry the amount of compute they scale out with it at the same time.”
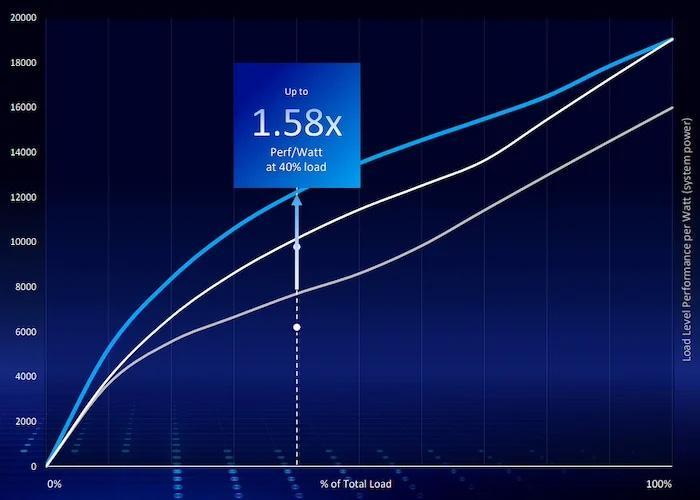
The Xeon 6 6700/6500 families are optimized to provide better power efficiency at all CPU loads, ensuring minimum TCO with any computational load.
Intel claims the new processors feature up to 1.5× better performance in AI inference compared to similar offerings. This performance also comes with better power savings, with a reported 68% TCO reduction and a 1.58× improved power efficiency at 40% loads.
Enabling Next-Gen Applications
The Xeon 6 family may provide power efficiency and improved performance in many applications. In more traditional use cases, the Xeon 6 processors’ scalability allows them to be deployed in HPC servers, AI inference applications, or secure compute environments. Designers can achieve a 5:1 or even 10:1 consolidation of their current server hardware for comparable performance in a smaller form factor or large leaps in overall performance.

Xeon 6 processors enable considerable consolidation, creating avenues for improved performance, smaller size, and better power efficiency.
The Xeon 6 can also be used to enable advanced applications, such as 5G and RAN deployment. In this use case, the Xeon 6 SoC can integrate processing, accelerators, and memory for an all-in-one solution. Compared to previous generations, the Xeon 6 SoC offers up to 2.4× RAN capacity and a 70% improvement in performance per watt, making the Xeon 6 an attractive candidate for the future of 5G and IoT applications.
Intel anticipates a smooth shift to using the Xeon 6 from previous generations or comparable hardware.
“Operators can begin implementing and benefitting from AI in the RAN today, right now, without needing costly additional hardware,” Rodriguez said.
Continuing Computing Momentum
In addition to the new processors, Intel has also released accompanying networking cards, which can reportedly achieve up to 200 Gb/s speeds while maintaining a secure environment. While the Xeon 6700/6500 has only just been unveiled, Intel already has its eyes on the future, with its latest processor lineup, “Clearwater Forest,” slated for release in the first half of 2026.
“As a general rule of thumb today, we've been saying roughly around 20 billion parameters or less is really the sweet spot for running generative AI inference on the CPU. Once you go past that level, you're really better off running it on a GPU or an ASIC—but then it's about choosing what is the best CPU to be the host in those accelerated systems,” Singhal said. “Our position on Xeon 6 is that we're the best CPU in the world for both use cases, whether it's for doing AI computations on the CPU or for the CPU you want to have as your host in an AI-accelerated system.”




