Arm Singles Out Next-Gen IoT With New Edge AI Platform
Last week, Arm introduced its Armv9-based Cortex-A320 processor and Ethos-U85 neural processing unit (NPU) to help advance edge AI computing. This combination forms the Armv9 edge AI platform, designed to improve machine learning performance and software flexibility for IoT applications.

The Armv9 Edge AI Platform.
Cortex-A320: An Ultra-Efficient Armv9 CPU for IoT
The Cortex-A320 is Arm’s first ultra-efficiency core based on the Armv9 architecture. With the new architecture, the system achieves a 10x increase in machine learning performance over its predecessor, the Cortex-A35, and delivers 30% higher scalar performance. These improvements are primarily driven by the integration of Scalable Vector Extension 2 (SVE2), which enables wider vector processing and optimizes the execution of AI workloads.

Block diagram of the Arm Cortex-A320.
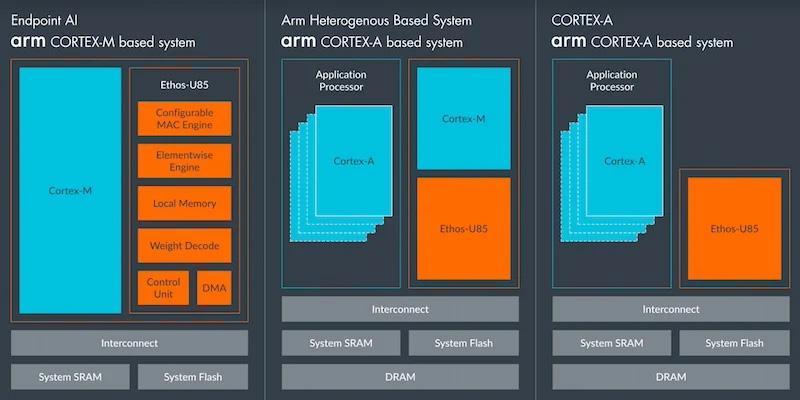
Designed with heterogeneous compute efficiency, the Cortex-A320 operates as part of a system that also includes the Ethos-U85 NPU. This approach dynamically distributes workloads based on computational demands to minimize latency and optimize power consumption.
“Our V9 Edge AI platform couples a brand new ultra-efficient Cortex A320 and our leading edge AI accelerator, the Ethos U85 neural processor, to deliver a true heterogeneous edge AI solution,” Williamson said. “It allows the IoT ecosystem to run the right workloads in the right place at the right time.”
The processor’s memory architecture has also been upgraded to handle larger AI models more efficiently to support improved addressable memory and multiple tiers of memory access latency. For scalability purposes, the Cortex-A320 can be grouped in clusters of up to four cores.
Ethos-U85: Arm's Most Advanced NPU
Arm calls the Ethos-U85 its most advanced neural processor to date, providing up to 4 tera operations per second (TOPs) at 1 GHz. Meanwhile, it improves power efficiency by 20% compared to the previous Ethos-U65 and U55 NPUs.
Different applications of the Ethos-U85.
One major enhancement is its native support for the transformer-based AI models increasingly used in vision processing and language-based AI applications.
Another significant shift in this generation is the direct integration between the Cortex-A320 and the Ethos-U85. This integration functionally eliminates the need for a separate Cortex-M controller to drive the NPU. The result is reduced system complexity, lower cost, and improved overall performance.
Leveraging Arm Kleidi
A major component of the new platform’s appeal is Arm Kleidi, a set of compute libraries designed to accelerate AI workloads on Arm CPUs without requiring additional developer effort. Previously introduced in Arm’s client markets, Kleidi has now been extended to IoT applications so developers can maximize AI performance without modifying their existing frameworks.
“Last year, we introduced this into the client markets,” Williamson said. “Kleidi AI is a set of compute kernels for developers of AI framework that provides them with this frictionless access to the best performance possible on an Arm CPU.”
Kleidi includes KleidiAI and KleidiCV to optimize machine learning and computer vision tasks, respectively. The libraries integrate with leading AI frameworks such as Llama.cpp, ExecuTorch, and LiteRT to provide up to 70% performance gains for ML workloads running on the Cortex-A320. The library also supports Neon and SVE2 optimizations for advanced vector processing to accelerate AI computation.
Implications for Edge AI and Future Applications
According to Arm, industry leaders, including AWS, Siemens, Renesas, and Advantech, have already expressed strong interest in adopting the new platform. AWS plans to integrate the Cortex-A320 with its Nucleus Lite runtime for constrained edge devices, while Siemens sees the platform as a foundation for secure, high-performance AI in industrial automation.
“AI at the edge is not only going to improve these commercially-driven use cases and benefit the people who use the devices, but I believe it’s got the opportunity to have profound effects on bigger, more global issues that touch all of us,” Williamson concluded. “For example, it has the potential to help us reduce the climate impact of human activity, monitor and improve biodiversity, and even revolutionize healthcare.”




