2024 Ultimate Guide to Coaxial Connectors: Types, Applications, and Selection Tips
This guide offers a 2024 overview of the diverse range of coaxial connectors, encompassing BNC, F-type, and SMA connectors. It delves into their applications and benefits, providing insights tailored for the current year. Our updated 2024 comprehensive guide aims to aid you in choosing the most suitable connector for your specific needs and in grasping their contemporary applications.
What is a Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cables, often referred to as "coax," are specialized electrical cables designed to transmit high-frequency signals with minimal interference and signal loss, making them ideal for use in a range of applications. These cables are constructed with a distinctive multi-layer design.
• A central conductor, often crafted from copper or steel coated with copper
• A layer of insulation, known as a dielectric, that encases the central conductor
• A conductive screen, commonly constructed from metallic foil or woven copper mesh
• A protective outer jacket for safeguarding
This concentric design, with all components sharing a geometric axis, gives coaxial cables their name.
Coaxial cables offer a number of advantages:
1. Effective long-distance signal transfer
2. Superior protection against electromagnetic disturbances
3. Robustness coupled with straightforward installation
4. Adaptability across a range of applications
Common applications of coaxial cables encompass::
• Distribution for cable television systems (CATV)
• Provision of broadband internet services
• Transmission lines for telephone trunks
• Connections for computer networks, such as Ethernet
• Conveyance of radio frequency (RF) signals
• Linking radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas
• Transmission of digital audio via S/PDIF
• Use in video equipment setups
Coaxial cables are available in a range of types, differentiated by their impedance levels and physical dimensions. The most prevalent impedances are:
• 75 ohms: Commonly utilized for video signal transmission and in home installations
• 50 ohms: Frequently employed in data communication and settings requiring moderate power handling
The standard cable sizes comprise:
• RG-6: Suitable for shorter transmission spans, up to 150 feet
• RG-11: Chosen for longer reaches due to superior performance
• RG-58, RG-59, and RG-213: Deployed across different applications based on specific needs
Common Coaxial Cable Sizes

There are a number of common sizes of coaxial cable, each designed for specific applications and signal transmission requirements. The "RG" designation stands for "Radio Guide," a term that originated in military specifications. The following are three common coaxial cable sizes:
RG-6: This cable is a popular choice for use in both residential and commercial settings, thanks to its versatility and performance. With a relatively thin overall diameter of approximately 0.275 inches, these cables feature a broad central conductor, thick insulation, and specialized shielding. These cables offer robust signal transmission capabilities and are suitable for high-frequency applications up to 1 GHz. Their flexibility makes them ideal for installation in ceilings and walls, and they are commonly used for cable TV, satellite TV, and broadband internet connections, with an effective range of up to 200 feet.
RG-11: This cable is designed for long-distance signal transmission in challenging environments. They have a larger overall diameter of approximately 0.405 inches and a thicker central conductor. These cables are enhanced with superior shielding, often in multiple layers, which provides excellent resistance to signal loss over long distances. These cables are suitable for high-frequency applications up to 3 GHz and are ideal for outdoor installations and long cable runs. RG-11 cables are commonly used in commercial settings, schools, and office complexes. They are effective for distances up to 600 meters, but are less flexible than RG-6, which makes installation more challenging.
RG-59: While it is less commonly used today, it still has specific applications. They have a thinner overall diameter than RG-6 and a smaller central conductor. Given their lower bandwidth capacity, these cables are best suited for low-frequency transmission over limited distances. RG-59 cables are frequently utilized in home audio/video applications and select security camera systems. RG-59 cables are more susceptible to signal loss and interference than RG-6, and are therefore not recommended for use with modern high-definition video or high-speed internet connections. Nevertheless, they continue to be employed in certain radio antenna applications and legacy systems.
When selecting a coaxial cable, it is essential to consider the required signal frequency, transmission distance, installation environment, and the specific application requirements. RG-6 is suitable for most residential applications. However, RG-11 may be necessary for long-distance or commercial installations, and RG-59 is primarily used in legacy systems or specific low-frequency applications.
What is a Coaxial Connector?

Coaxial connectors, also known as RF connectors, are specialized electrical components designed to work with coaxial cables. Their principal functions are to terminate cables, connect devices to power supplies, and join cables together while maintaining the cable's shielding integrity. These connectors are essential for maintaining signal quality in a variety of applications.
The typical structure of a coaxial connector comprises a center pin or socket for the inner conductor, an insulating layer, an outer conducting sleeve, and a coupling mechanism. This design guarantees the maintenance of the coaxial cable's concentric structure, which is vital for ensuring signal integrity.
Some specialized coaxial connectors offer additional features, such as built-in switches that automatically disconnect internal batteries when an external power supply is connected, providing an extra level of security and convenience. This functionality is particularly beneficial in portable electronic devices.
Common Coaxial Connector Styles
There are numerous types and sizes of coaxial connectors available on the market, each designed to meet specific needs across a range of applications. The variety of connector types reflects the extensive range of applications for which coaxial cables are used, including consumer electronics, industrial, and military. Each connector is meticulously designed to integrate seamlessly with its corresponding cable type, ensuring optimal signal transmission and minimal interference.
These connectors are designed to withstand a variety of environmental challenges. It is essential that they be resilient against physical stressors such as impact, pressure, and vibration. Furthermore, many are designed to function reliably in extreme temperatures, making them suitable for outdoor installations or use in harsh industrial environments. This robustness is essential for maintaining consistent performance over time, even under demanding conditions.
In the context of radio frequency (RF) transmission, coaxial connectors assume a particularly critical role. These specialized connectors are designed to provide consistent electrical resistance at the connection point between cables. This consistency is essential for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing loss. However, the precision required for these RF connectors also makes them somewhat delicate. It is essential to handle these connectors with care during installation and maintenance to prevent damage that could impair their performance.
These connectors are renowned for their durability and reliability in outdoor and high-moisture settings. Their threaded design ensures a secure connection, making them an optimal choice for applications where signal integrity is of the utmost importance. The "7/16" designation in the product name refers to the approximate outer diameter of the connector in millimeters.
Commonly used in:
- Radio base stations - used to help maintain consistent signal quality in varying weather condition.
- Broadcasting equipment - support the transmission of high-frequency signals with minimal loss.
BNC (Bayonet Neil-Concelman) connectors are a compact and versatile type of RF connector that is widely used in a variety of electronic applications. These connectors are distinguished by their rapid-connect/disconnect bayonet locking mechanism, which enables seamless and secure connections.
The design of BNC connectors makes them an ideal solution for applications requiring:
- The ability to rapidly connect and disconnect. The bayonet mechanism enables a quick quarter-turn to lock or unlock the connector, which is particularly beneficial in dynamic environments where time is of the essence.
- Ensures secure connections: Despite their quick-release design, BNC connectors provide a stable and reliable connection, resistant to accidental disconnection, ensuring a secure and dependable link.
- Consistent impedance: Typically designed for 50- or 75-ohm systems, BNC connectors are suitable for maintaining signal integrity in a variety of RF applications.
- Moderate frequency range: While BNC connectors are not suitable for very high frequencies, they perform well up to about 4 GHz, making them a versatile choice for many common applications
F-connectors, often referred to as F-type connectors, are a widely used solution for transmitting electrical signals to television sets and other audio-visual equipment. These connectors are designed to provide a reliable connection for coaxial cables, ensuring optimal signal quality for both analog and digital transmissions.
F connectors are especially compatible with RG6 and RG59 coaxial cables.
- RG6 cables are the preferred option for high-frequency applications, such as satellite and cable television, due to their superior shielding and lower signal loss.
- RG59 cables are typically utilized for standard-definition video and shorter cable runs, making them well-suited for less demanding applications.
FME connectors, an acronym for "For Mobile Equipment," are compact, threaded RF connectors designed specifically for use in mobile and portable devices. These miniature connectors provide a reliable solution for applications where space is limited and a secure connection is essential.
Originally developed to meet the growing demand for smaller, lightweight connectors in the mobile communications industry, FME connectors have become a widely used solution in various mobile and portable equipment.
Their applications include:
1.Cellular Antennas and Boosters
2. GPS Devices and Antennas
3. Wireless Modems and Routers
4.Portable Radio Equipment
5.Automotive Telematics Systems

MBX Connectors
These connectors are renowned for their durability and reliability, and are therefore commonly utilized in a wide range of RF applications, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and instrumentation.
One of the key advantages of MBX connectors is their robust construction, which enables them to withstand challenging environmental conditions and mechanical stress. Their durability makes them an ideal choice for demanding applications where reliability is of the utmost importance.
MCX connectors, short for Micro Coaxial, are designed to meet the growing demand for miniaturization in electronic devices. These connectors provide a space-efficient solution for applications where there is limited space on circuit boards or device housings.
The MCX connector design incorporates a snap-on mechanism that allows for quick and easy attachment and removal, providing a convenient solution for users. This feature is especially advantageous in settings where rapid connections and disconnections are required, such as in testing and prototyping scenarios. Despite their compact design, MCX connectors offer excellent electrical performance, supporting frequencies up to 6 GHz in certain configurations.
Also referred to as N-type connectors. One of the most notable attributes of N connectors is their weatherproof design. This feature makes them an excellent choice for outdoor applications where exposure to moisture and other environmental factors is a concern. The connectors achieve this through a threaded coupling mechanism that provides a secure, water-resistant seal when properly tightened.
N connectors are used in a variety of fields, but they are particularly well-suited for radio transmission equipment. Their applications include:
• Base station antennas for cellular networks
• Broadcast transmitters and receivers
• High-power RF amplifiers
• Microwave systems and test equipment
QMA Connectors The "Q" in QMA represents "quick," emphasizing the primary advantage of these connectors: the ability to establish rapid connections without the need for tools like torque spanners.
These connectors feature a distinctive push-pull locking mechanism, enabling rapid attachment and detachment. This design significantly reduces installation time and simplifies maintenance procedures, especially in environments where frequent connections or disconnections are necessary. While QMA connectors are designed for rapid connection, they also provide a secure and stable link once engaged.
They are highly resistant to vibration and mechanical stress, making them ideal for use in challenging environments. This durability is particularly beneficial in outdoor and mobile applications, where equipment may be subject to constant movement or environmental challenges. The connectors are also designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, making them suitable for exposed installations.
SMA (SubMiniature version A) connectors are compact, precision-engineered RF connectors that are integral to a wide range of electronic applications. Although they may appear similar to F-type coaxial connectors at first glance, SMA connectors are unique in both design and application. The primary physical distinction between the two is their slightly smaller size, with SMA connectors typically measuring approximately 2mm less in diameter than F connectors.
They provide reliable connections for frequencies up to 18 GHz in standard configurations, with some specialized versions capable of operating at even higher frequencies. The threaded coupling mechanism of SMA connectors provides a secure connection, ensuring resistance to vibration and accidental disconnection.
Subminiature Version B (SMB) connectors offer an optimal balance between size and performance. These connectors are distinguished by their user-friendly snap-on coupling mechanism, which enables rapid connections and disconnections without the necessity for tools.
The design of SMB connectors makes them an optimal choice for applications where space is limited and frequent connections or disconnections are required. Typically, these connectors operate effectively at frequencies up to 4 GHz, with some specialized versions capable of higher frequency performance.
Subminiature Version C (SMC) connectors represent another advancement in the line of miniature RF connectors, following the introduction of their SMA and SMB counterparts. These connectors are designed to provide a compact solution for RF connections while offering enhanced protection against environmental factors.
The most distinctive feature of SMC connectors is their screw-type interface, which sets them apart from other types of connectors. The threaded coupling mechanism provides a secure and stable connection, which is particularly beneficial in applications that are subject to vibration or mechanical stress.
The key features of SMC connectors include:
1. The threaded design allows for an airtight closure, effectively protecting against leakage and potential damage from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and other contaminants. This makes SMC connectors an optimal choice for use in harsh or exposed environments.
2. The compact size of the connector is an additional benefit. While slightly larger than SMB connectors, SMC connectors are still considerably smaller than standard SMA connectors, making them an optimal choice for applications where space is at a premium.
3. Reliable Performance: SMC connectors are designed to operate effectively at frequencies up to 10 GHz, with some specialized versions capable of higher frequency performance.
4. Durability: The robust construction and secure locking mechanism of SMC connectors contribute to their longevity and reliability in demanding applications, making them an ideal choice for use in challenging environments.
TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman) connectors represent an evolution of the popular BNC connector design. They have been specifically engineered to meet the demands of more challenging environments, particularly outdoor applications. The TNC connector offers the quick-connect convenience of the BNC, along with enhanced durability and weather resistance.
TNC connectors are available in both 50-ohm and 75-ohm impedance versions, making them suitable for a wide range of RF applications. Their design allows for straightforward field installation and maintenance, which is particularly beneficial in remote or challenging locations.
These variants of the basic BNC connector are used with triaxial (triax) cables. They offer enhanced bandwidth but are typically more costly.
The key features of this product are as follows:
• An additional layer of insulation
• An extra conducting sheath
Twinax connectors are a doubled variation of the BNC connector and are used to prevent signals from being mixed. These are also referred to as Twin BNC connectors.
The key features are as follows:
• A latching mechanism
• Crimp connectors for straightforward installation
• Both male and female contact points
UHF connectors, which stand for Ultra High Frequency connectors, were originally designed for use in high-frequency applications. However, as technology has advanced, their primary applications have shifted, and they are now predominantly utilized with lower frequency devices. Despite their name, UHF connectors are often used in contexts where their robust design and reliable performance are more important than their frequency rating.
One of the most common applications of UHF connectors is in the video connectivity of military equipment. Their robust construction and ability to maintain a secure connection make them an ideal choice for the challenging environments often encountered in military applications. UHF connectors are capable of handling significant power levels and are designed to withstand harsh conditions, including vibration and extreme temperatures, making them an ideal choice for a range of applications.
The Ultraminiature Coax Connector (UMCC) is utilized for frequency signals up to 6 GHz in highly compact environments, such as laptop circuit boards and embedded circuitry.
Commonly used to:
- Make connections to GPS
- Connect to Wi-Fi antennas
Selecting the Appropriate Coaxial Connector
When selecting a coaxial connector, consider these key parameters:
- Voltage requirements
- Environmental conditions
- Frequency range needed
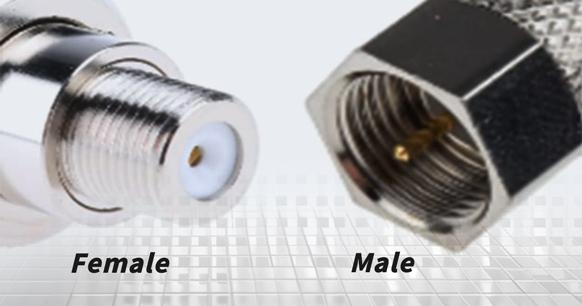
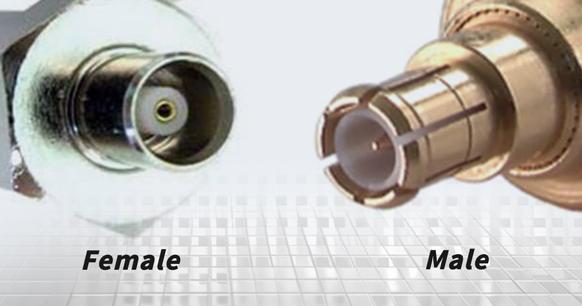
- Connector gender (male or female). Male connectors feature protruding metal pins, while female connectors have recesses designed to receive these pins.
Understanding Coaxial Connector Genders
In the field of electrical engineering, connectors are typically classified as either male or female. Male connectors feature protruding pins or metal inserts that are inserted into the corresponding indentations or slots of female connectors. This mating process guarantees the correct flow of signals or power and prevents unsafe installations or interference.
Female connectors are typically more durable and are often placed in crucial areas, while male connectors are used on easily replaceable cables. It should be noted, however, that these gender terms may not apply to all electrical standards, particularly in the case of low-voltage domestic appliances.
Male Coaxial Connectors
These connectors include a central pin that is meant to engage with the female connector, accompanied by a spring-loaded electrical contact on the periphery.
Female Coaxial Connectors
Female connectors are equipped with a metallic tube (tip) to accept the male pin, enveloped by an insulating material and an outer cylindrical part (barrel or sleeve) that acts as an electrical contact.
Genderless Coaxial Connectors
Referred to as combination connectors, these adaptable connectors possess both male and female components. They are capable of connecting with either male or female connectors of the appropriate size and type, facilitating rapid reconfiguration in intricate setups. Nevertheless, they might not be fit for systems that necessitate regulated unidirectional current flow for safety or operational purposes.
Genderless connectors exhibit an inverse electrical polarity, featuring a pin extending from the female end and a corresponding slot in the male end to receive this pin.
Summary
Coaxial connectors are essential components in RF and telecommunications, available in various types such as BNC, F-type, N-type, and SMA. Each type of connector has specific applications, from TV and radio to military and aerospace. These connectors are available in male, female, and genderless configurations, designed to maintain signal integrity and provide secure connections. When choosing a connector, it is important to consider factors like voltage, frequency, environment, and gender type. Understanding the characteristics of different connectors helps in selecting the right one for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance in diverse settings from home entertainment to professional communications systems.