TI Reveals Radar Sensor and Audio ICs to Elevate Auto In-Cabin Designs
Today, ahead of CES (opening tomorrow), Texas Instruments (TI) has announced a suite of semiconductor technologies aimed at reshaping the in-cabin automotive experience. The new offerings include the AWRL6844 60-GHz mmWave radar sensor and the AM275x-Q1 and AM62D-Q1 processors, which integrate advanced AI capabilities, audio processing features, and novel modulation technologies.

TI's new ICs are aimed at enhancing the in-cabin driving experience.
All About Circuits spoke to Texas Instruments’ representatives Mark Ng, Yariv Raveh, and Sonia Ghelani to learn about the releases firsthand.
A Multifunctional In-Cabin Solution
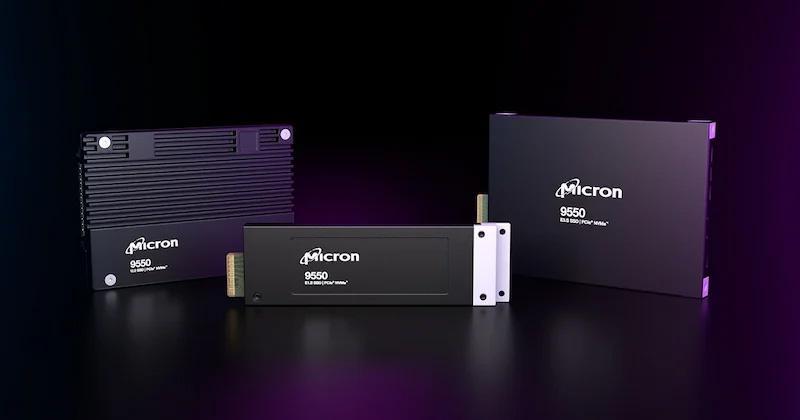
Texas Instruments is calling the AWRL6844 the industry's first single-chip, 60 GHz mmWave radar sensor that can support three critical in-cabin sensing applications. Designed with edge AI capabilities, the sensor leverages an on-chip accelerator and DSP to process data locally for applications like seat belt reminders, child presence detection, and intrusion detection.
“By integrating three sensing systems into a single chip, the AWRL6844 reduces system complexity and cost by about 50% compared to current in-cabin monitoring architectures,” Raveh explained.
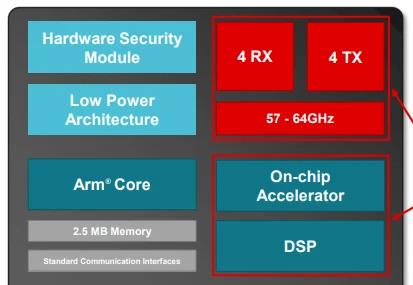
Block diagram of the AWRL6844.
Edge AI is central to the AWRL6844’s performance. To this end, the chip incorporates a 4 x 4 antenna array to generate high-resolution spatial data, which feeds into neural network algorithms optimized for real-time classification and detection. TI claims the sensor achieves 98% accuracy in distinguishing between human occupants and non-living objects. Similarly, child presence detection uses AI models to identify micromovements, such as respiration, with a reported 90% classification accuracy. Additionally, the sensor’s low-power architecture consumes less than 50 mW during active monitoring.
Scalable Audio Processing
TI’s AM275x-Q1 MCUs and AM62D-Q1 processors integrate the company’s next-generation C7x DSP core for automotive audio systems that deliver high-performance processing with scalability across vehicle tiers.
“With our new MCUs and processors, TI enables premium audio features across the OEM's vehicle lineup by providing multiple device and architecture options, all leveraging the same software investment," Ghelani said.
For entry-level vehicles, the AM275x-Q1 MCU provides a DDR-less architecture with up to 4.5 MB of L2 memory and 6 MB of L3 memory. This configuration supports premium features such as active noise cancellation (ANC), real-time audio tuning, and acoustic vehicle alerting systems (AVAS) with minimal hardware requirements. By focusing on efficient memory use, the processor enables up to 32 audio channels without external memory.
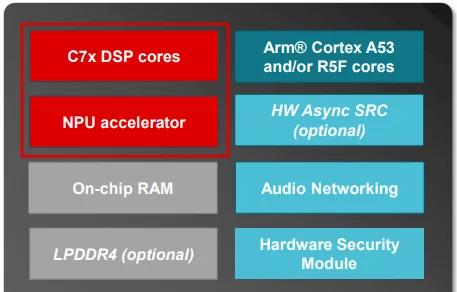
Block diagram of the AM274x-Q1.
In luxury vehicles, the AM62D-Q1 processor expands these capabilities with a DDR4 interface and larger memory bandwidth. TI optimized this configuration for applications requiring high-speed access to external storage, such as immersive 3D audio, advanced sound synthesis, and simultaneous multi-zone audio processing. The integrated neural processing unit (NPU) further enhances the system by running AI-driven audio algorithms that adapt soundscapes to passenger layouts.
Both processors incorporate functional safety features, such as hardware security modules and compliance with ASIL standards.
Audio Amplification with 1L Modulation Technology
Traditional Class-D amplifiers use two LC filters per channel to manage high-frequency switching noise. The TAS6754-Q1 Class-D audio amplifier introduces TI’s proprietary 1L modulation technology that reduces the number of inductors per audio channel by half.
“TI's proprietary 1L modulation technology maintains Class-D performance with half the number of inductors, leading to smaller, lighter designs that reduce costs without sacrificing audio quality,” Ng said.
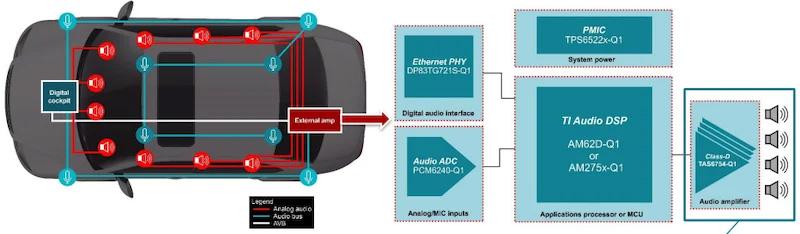
TI’s proposed in-vehicle audio system.
Reducing passive components decreases overall system size, weight, and cost, offering a 50% smaller footprint and proportional cost savings. The solution also integrates real-time load diagnostics for maintaining consistent sound quality in vehicles with varying speaker configurations.
Bridging Cost and Performance
TI aimed to balance cost, performance, and system complexity in its new automotive solutions. By integrating multiple functions into single-chip solutions, such as the AWRL6844 and AM275x-Q1, TI enables OEMs to consolidate components, thereby reducing the total bill of materials.
The radar sensor, for instance, replaces ultrasonic and ultra-wideband sensors, which traditionally require multiple calibration steps and higher per-unit costs. Similarly, the AM275x-Q1 and AM62D-Q1 processors eliminate the need for external audio processors, enabling premium features across all vehicle tiers with a unified software investment. TI estimates that these solutions can reduce implementation costs by as much as $20 per vehicle.
TI’s Vision for the Automotive Industry
As the automotive sector transitions toward software-defined vehicles and increased electrification, TI’s edge AI-enabled radar sensor and scalable audio processors represent a step forward. By combining advanced processing capabilities with energy-efficient designs, these solutions address the dual challenges of regulatory compliance and consumer demand for enhanced in-cabin experiences.




