Silicon Labs Rolls Out ‘Lite’ Low-Power Bluetooth LE SoCs
Silicon Labs recently introduced its new BG22L and BG24L low-cost Bluetooth chips targeting applications ranging from asset tracking to geofencing. Silicon Labs optimized the BG22L for high-volume, cost-sensitive, and low-power applications while outfitting the BG24L SoC with additional support for channel-sounding technology and AI/ML acceleration.

The BG22L and BG24L can be used in asset-tracking applications.
The BG22L for Low-Cost Applications
Silicon Labs designed the EFR32BG22L Wireless Gecko family of SoCs for low-cost, low-energy applications. The single-die solution combines a 38.4-MHz Cortex-M33 processor with a 2.4-GHz radio. Depending on the specific model number, it can have up to 352 KB of Flash and 24 KB of RAM. All model numbers are packaged in a 4 mm x 4 mm QFN package. To reduce overall energy consumption, the chip supports several operating modes, with each mode activating specific parts of the chip.
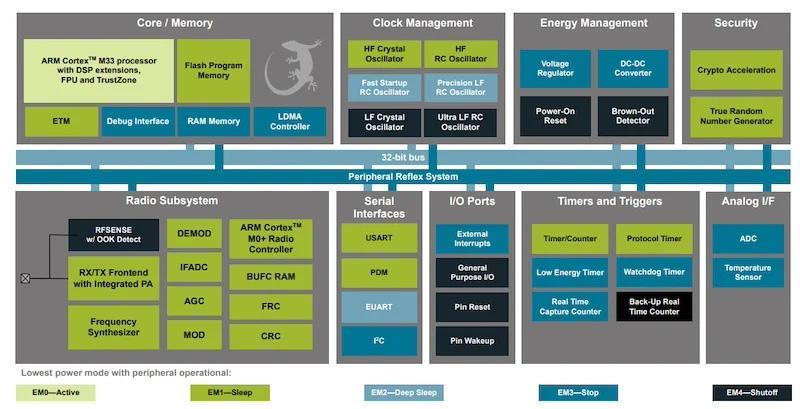
Block diagram of EFR32BG22L SoC.
The Cortex M33 processor is only on in “EM0–Active” mode. When the chip is in other states, such as “EM1–Sleep” and “EM2–Deep Sleep,” only certain parts of the chip remain on, such as the Arm Cortex M0+ Radio Controller in sleep mode and the I2C interface in deep sleep mode. Silicon Labs claims that the BG22L leverages these low-power modes to enable a ten-year battery life. An integrated precision low-frequency RC oscillator (PLFRCO) also eliminates the need for an external oscillator.
BG24L SoC With AI/ML and Channel Sounding
While the EFR32BG24L (BG24L) is also optimized for low-cost, low-energy applications, it includes features not present in the BG22L chip. For starters, the TX supports more protocols, including Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE), Bluetooth Mesh, a proprietary 2.4-GHz protocol, and channel sounding. Channel sounding is a technology that estimates the distance between two Bluetooth devices using two techniques—one based on round-trip time (RTT) and the other based on phase-based ranging (PBR).
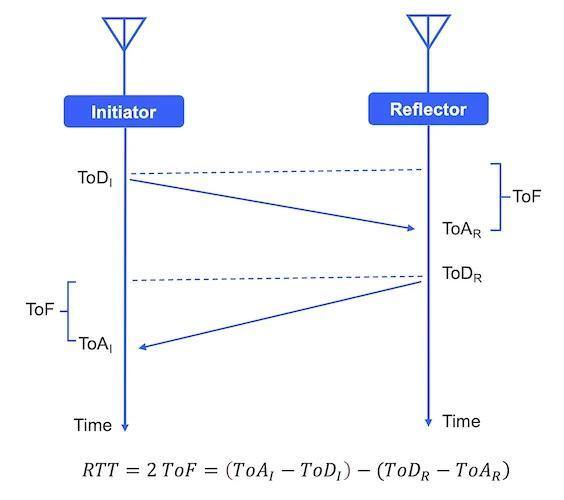
Round-trip time channel sounding.
As its name implies, the RTT technique uses the total time of a transmitted and reflected signal to determine the distance between the initiator and reflector. PBR, on the other hand, uses the delta in phase of the transmitted and reflected signal to determine the total distance. Due to the complexity of measuring and analyzing phase-based information, Silicon Labs says PBR is a highly secure technology.
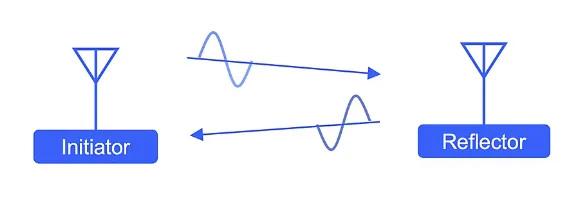
Phase-based ranging (PBR) channel sounding.
Tools for Location Monitoring
Silicon Labs says the channel-sounding capabilities of the BG24L make it useful for asset-tracking and direction-finding applications—for example, monitoring the location of equipment and personnel on industrial and commercial sites. On a construction site, equipment can use channel sounding via Bluetooth to report its location to a centralized hub.
Silicon Labs says that the AI/ML capabilities of the BG24L also make it well-suited to predictive maintenance applications. The BG22L and BG24L are not the only SoCs on the market with channel-sounding technology. Nordic Semiconductor also offers a full range of Bluetooth SoCs with channel-sounding technology for IoT applications.




